Scripts & User config
Elrond provides scripts designed to streamline the process of installing an Elrond node. You will start by getting a copy of the latest version of the scripts from GitHub, and configure it to match your local setup.
Download the Elrond Scripts
cd ~
git clone https://github.com/ElrondNetwork/elrond-go-scripts-mainnet
Configure the scripts correctly
The scripts need a few options to be set in order to work correctly.
First and foremost, you need your exact username on the machine. You can find out your current username by using the whoami command, which will print it out:
whoami
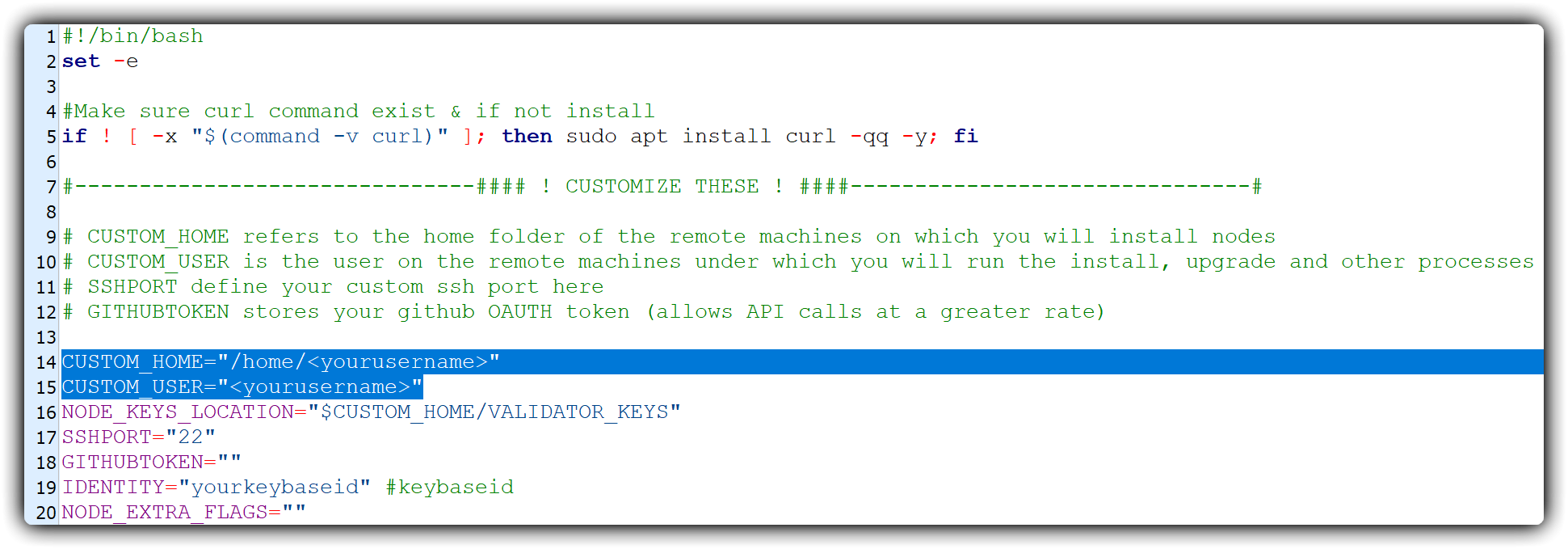
Next, we need to edit the variables.cfg file and add your username in the following variables:
CUSTOM_HOME, which refers to the folder on the computer in which you will install your nodesCUSTOM_USER, which is the username on the computer under which you will run the installation, upgrade and other processes
Open variables.cfg in the nano editor:
cd ~/elrond-go-scripts-mainnet/config
nano variables.cfg
Change the variables CUSTOM_HOME and CUSTOM_USER, as indicated in the screenshot:
Replace
Save the file and exit :
- if you’re editing with nano, press
Ctrl+X, thenyand thenEnter - if you’re editing with vi or vim, hold down
Shiftand pressztwice
Ensure user privileges
Your user should be sudo capable, so that it doesn't ask a password every time it executes something. If you already know this to be true, skip ahead. Otherwise, you need to add your username to a special list.
So let's add it to the overrides:
sudo visudo -f /etc/sudoers.d/myOverrides
Now navigate to the end of the file, by pressing Shift + G. Now press o to add a new empty line, and type the following, replacing username with what you got from running the whoami command:
yourusername ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL
Conclude by pressing Esc, then save and close the file by holding down Shift while pressing z twice.
Your user should now be able to execute sudo commands.
